I snatched this view at Bodrum this summer. I wanted to share with you 🙂
Monthly Archives: Kasım 2016
Chapter 8 and 9
WESTERN EUROPE after the ROMAN EMPIRE
When the western history is wrote at 15th century, the thinkers of Renaissance describe the period which is between glorious ages of the civilization of GREEK and ROME and their era of enlightenment as dark ages. However the dark ages are not cultural infertility. There were a lot of attempts to develop. The one of attempt is Carolingian Renaissance which is began by Charlemagne.Charlemagne emperor had no capital city but the main area was in Cologne and Aachen. This city became a cultural center of Europe rapidly. With the effort of rebirth is concluded a building of a octagonal chapel which is imitated by San Vitale Byzantium Emperor Church. This building is designed by Metz Odo at 792-805 and is built of face stone. The architecture of house and castle had a pyramid order like a hierarchical system. All units submitted peoples which had high authority from themselves. Also for security, wooden towers changed as a stone tower.
( the photos taken by : http://blogs.hisarschool.k12.tr/orkansezer/2013/12/30/gunumuzu-bilmek-icin-gecmisi-bilmek-gerekir/)
Medieval monasteries became a cultural, political and agricultural center. Saint-Martin-du-Canigou Monastery was small and very good isolated example. It is built on steep knap. It had a irregular plan also the cast light was dim. Saint-Gall Monastery drawing is the oldest plan example because it is very important. It had a lot of altars and is rotated from west to east.Also it included inn like service buildings.
Romanesque churches had massive masses and small windows. Because of the similar architectural element between roman architecture and Romanesque architecture, this style is named Romanesque Architecture. Saint Micheal church is an example of molar Romanesque Architecture and there was no city walls.
Pilgrimage Church are ornamented by sculptures which symbolized the eternal life. On the way of pilgrimage, there are two monastery churches which characterize the Romanesque Pilgrimage Church. These monasteries are Sainte – Foy church at Conques and Saint Sermin Church at To louse. Sainte Foy Church;
There were stone vault at all interior spaces. It had barrel vault which is reinforced by cross belt and also luminous intensity is low.
Saint- Sermin Church;
is vowed Sermin who the first patriarch at Toulouse. It is covered with vault. Saint- Sermin is more complex as a spaces than Sainte-Foy, also they have similar naves. Similarly luminous intensity is low.
Prejury 1
My strategy was “orientation of different experiences”. I created different experiences on my path and at the and of path, I created an artificial hill about 15 meter long. Also there were spaces which include different experiences on my path. Jury said that about my artificial hill, it is very high and very harsh to climb. Also it’s slope is very much for human and this hill dominate all project so hill marginalize other spaces. Also these spaces which is on my path are not related between each other also and hill.
Also I used elements which had different colors to determine experiences and jury comment that why do you used different colors, they do not show any changes.
My spaces where are at on my path are located according to my axis. First axis continue to north and it break it continue the west as second axis and the last there was a axis which is parallel to first axis for visibility.
My spaces on the path orient the people from one to another and these spaces include the my experiences which observe at Göreme. I grafted my experiences the on spaces which are on the path. Jury said that these experiences are not refer each other, it looks like funfair. These are my experiences;
Also I designed my artificial hill with 3 different experiences all I added shade shadow conditions also to sit and walk places which have different sizes for human’s scale.
Also jury ask that “What was the aim of it? , what is served us?, We must always think about reason what is here, why is here and what serve us?”. I think that I should pay attention the scale of human’s, also the relations of my spaces which are on the path. My strategy was the acceptable for my aim, because I wanted to orient people and get horizon line on landscape. Also when people walk on my path they could observe different experiences which I graft from at Göreme. So My strategy is orientation of different experiences.
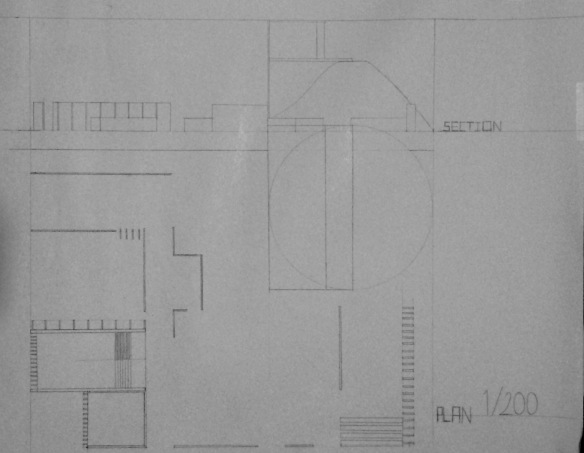
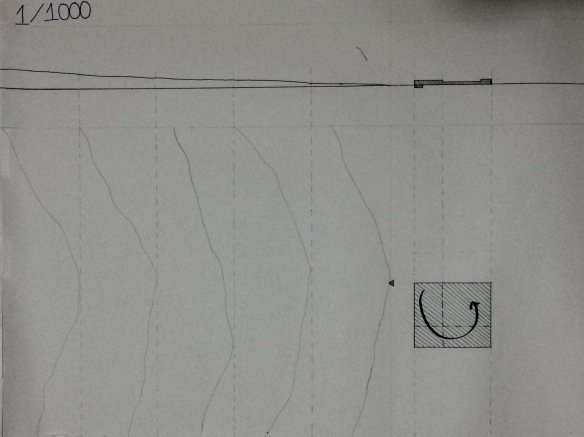
Here is my drawings which are section and plan also diagrams.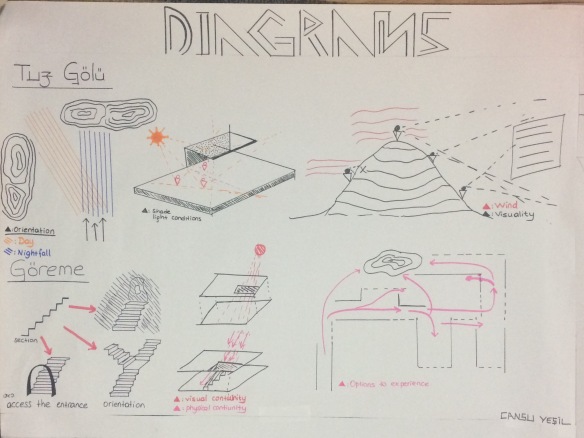
800-1200
The aim of Islam religion promulgate the teaching of Prophet Muhammad. Islam spread as an urban phenomenon tied to military and political power. The mosque provided the new religious center upon of the cities under Islamic rules. Also they are generally built as a multi columned prayer hall.
The minaret, a thin tower for the muezzin to call loyal to prayer, added a new vertical axis to urban skylines. Despite this obvious irregularity, all of Islam shared an underscoring sense of order in the circular orientation of mosques, tombs and prayers toward the theological mainstay of Mecca. During the seventh century Islam spread swiftly, extirpating various pagan cults while pursuit to transform Jews and Christians through sophisticated convincing, economic incentives and military force. Mecca had long been a major cult site for nomadic tribes of Arabia. Impressive religious pilgrims to the Kaaba, a cubical and granitoid house including many idols, involving a inscrutable black meteorite. Muslim pilgrims circumambulate the Kaaba seven times as the exalted non-resistance to God. As the focus of Muslim prayers, the Kaaba shows the association of the loyalty. Aside from the Kaaba in Mecca, Muhammad straight-forwardly, influenced the conversion of his own house in Medina into the new religion’s first mosque ( place of prostration).
The mosque of the prophet in Medina probably resembled a small traders caravansary, Muhammad’s modest approach to architecture echoed his nomadic origins. The first mosques are built simple architectural elements without apses, side chapels, ambulatories, crypts, baptisteries or choirs. The side hall ways and the north archway of the Great Mosque of Damascus carry arched with explicit horses shoe shape, can descent inland above the imposts. The motif became largely associated with Islamic monumental architecture.
Southeast Asia and Southern India
Angkor Wat is a temple complex in Cambodia and the largest religious monument in the world. Furthermore Bagan is the ancient city where is in Mandala Zone. The kings of Bagan and Cambodian Khmer were modern. In Bagan, about 2000 temple were built, one of the example is the head of Angkor Wat (12th century). It was in the capital city of old Khmer city and also the most big temple all Hindu temples. It was surrounded by broad ditch, gradual and rectangular complex. Also it had symbolic details which is relevant religion. Ancient Bagan City was built with bricks which are made of dusty soil. The city had thousands dome. Stu pas, Pagodas and Temples reflect a lot of different architectural touch.
Pagoda of Swezigon, the first example of pagoda for new pagoda buildings. It was covered with gold panels and the iam of pagoda was not worship, the aim was the relics of Buda could hide in this pagoda.
Origami Hyperbolic Parabola
I tried to make hyperbolic parabola with origami. First I used square paper and I started to fold. Here is my first origami.
My Catalog Work
Finding Strategy Process
We studied analyzes where at Salt Lake and Göreme. We created a catalog which is contained our experiences at our trip. After these analyzes we thought on strategy for our project because o that we observed lack things in Salt Lake and to provide experiences we drawn sketches. I drawn about orientation, visibility, light air conditions and boundaries.
300-600
Gupta India
Indian temple builders (from 1st to the 8th centuries) carved into rock reefs or out of stacked stones, making an art of subtraction. Subtraction as a design method allowed one to forgo such functional criteria as foundations, support systems, and roofs but required creative strategic organization for the displacement of material. The age of the Gupta inspired the great cave monasteries, the sublime rock-cut temples carved from single masses of stone, and the first important masonry temples built like pyramids over small sanctuaries. The caves at Bhaja about 100 km southeast of Mumbai had a horses shoe shaped arch where entrance of caves with struts(support) carved under its recessed gable in imitation of wooden purlins. The original wooden entry door and clerestory window that protected the entry have long disappeared exposing its longitudinal cavern. Octagonal columns had u shaped nave. At the end of the axis of the chaitya hall at Bhaja a stupa rests on a cylindrical pedestal, capped with a square harmika. The walls were polished smooth and gentle to the touch. The largest and most ornate of the early rock-cut chaitya halls was built around 120 CE at Karli, not far from Bhaja. During the Gupta Period of the 4th and 5th centuries the same carving techniques used at Karli appeared the production of freestanding temples.
The sex of the Hindu temples: in the 6th century in India, the sexualization of architecture appeared clear to all. Among the most common cut object was the lingam, a literal phallus, sometimes embedded with the likeness of the god Shiva. During the Gupta period the first freestanding Hindu temples sheltered a garbha griha, meaning “womb chamber”. The cult of the goddess Mahadevi was represented by the yoni, a vulval form. During the Gupta Period a Hindu priest compiled the Kama Sutra a synthesis of various treatises on the art of love.
Hi!
300 – 600
Emperor Constantine transport the capital from Rome to Byzantium at 330 and after that at 311, emperor Galerius embrace Christianity completely. New religion created a new aesthetic. In this way, the art of Byzantium developed. Religion influence the religious architecture. Firstly the building of Pagan temples are stopped and the first churches are buildings. First churches are derived from Rome Basilicas. In Constantine age, churches which are Betleem, Hagia Irine, Hagia Sophia, Pietro and Paolo were not vaulted. They were wooden basilicas. When Christianity became empire religion, three types churches were built
1) Basilicas
2)Central Planing Building
3)Combined Planning Building.
Basilicas: In the temple of Pagan, there was only sculpture of god and were not public. They had low clearance. The first basilicas were Santo Mario Maggiore and the ancient Rome Basilica.
Central Planing Building: Baptism: Ham-mam plans were used for baptism plan because there were baptism pool at middle of plan. as an example : San Giovanni Lateraro baptism and Theodoric Tomb .
Combine Planing Building: In these building, there were the mix of basilicas and central planing buildings.
San Paolo Basilica: The biggest church which type is basilica. San Paolo Basilica was made with the request of Constantine. On the bottom side there was bema and in main nave there was absid.
First Christian center is Byzantium. Whereas the Byzantium was a city of Rome, it had Greek cultural elements. After the building basilicas, domed Byzantine tone developed. The emperor abounded in material which were ashlar, timber block, and clay. also it ornamented with marbles and mosaics. Door and windows were generally round and arched.
Hagia Sophia: It was made with the request of Justin yen. It had rectangular shape, also the purpose of architect was creating functional and moving spaces. Arched and domes provide the purpose of architects.
























































